List of unsaturated fatty acids
| ω−n | Common Name | Lipid Numbers | Δn | Structural Formula | Trans or Cis | Naturally Occurring in |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ω−3 | α-Linolenic acid | C18:3 | Δ9,12,15 | CH3CH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CH(CH2)7COOH | cis | flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts[1] |
| ω−3 | Stearidonic acid | C18:4 | Δ6,9,12,15 | CH3CH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CH(
CH2)4COOH |
cis | seed oils of hemp, blackcurrant, corn gromwell [citation needed] |
| ω−3 | Eicosapentaenoic acid | C20:5 | Δ5,8,11,14,17 | CH3CH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2
CH=CH(CH2)3COOH |
cis | cod liver, herring, mackerel, salmon, menhaden and sardine [citation needed] |
| ω−3 | Cervonic acid | C22:6 | Δ4,7,10,13,16,19 | CH3CH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2
CH=CHCH2CH=CH(CH2)2COOH |
cis | maternal milk, fish oil[2] |
| ω−6 | Linoleic acid | C18:2 | Δ9,12 | CH3(CH2)4CH=CHCH2CH=CH(CH2)7COOH | cis | peanut oil,[3] chicken fat,[4] olive oil[5][6] |
| ω−6 | Linolelaidic acid | C18:2 | CH3(CH2)4CH=CHCH2CH=CH(CH2)7COOH | trans | partially hydrogenated vegetable oils | |
| ω−6 | γ-Linolenic acid | C18:3 | Δ6,9,12 | CH3(CH2)4CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CH(CH2)4COOH | cis | borage oil, black currant oil, evening primrose oil[7] and safflower oil[8] |
| ω−6 | Dihomo-γ-linolenic acid | C20:3 | Δ8,11,14 | CH3(CH2)4CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CH(CH2)6COOH | cis | only in trace amounts in animal products[9][10] |
| ω−6 | Arachidonic acid | C20:4 | Δ5,8,11,14 | CH3(CH2)4CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2
CH=CH(CH2)3COOH |
cis | |
| ω−6 | Docosatetraenoic acid | C22:4 | Δ7,10,13,16 | CH3(CH2)4CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2
CH=CH(CH2)5COOH |
cis | |
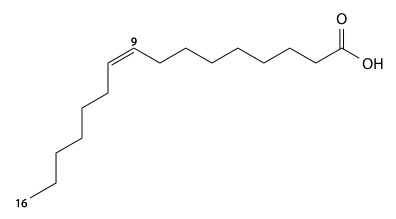
| ω−7 | Palmitoleic acid | C16:1 | Δ9 | CH3(CH2)5CH=CH(CH2)7COOH | cis | macadamia nuts[11] |
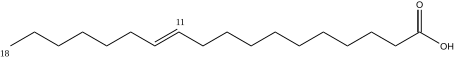
| ω−7 | Vaccenic acid | C18:1 | Δ11 | CH3(CH2)5CH=CH(CH2)9COOH | trans | dairy products such as milk, butter, and yogurt[12] |
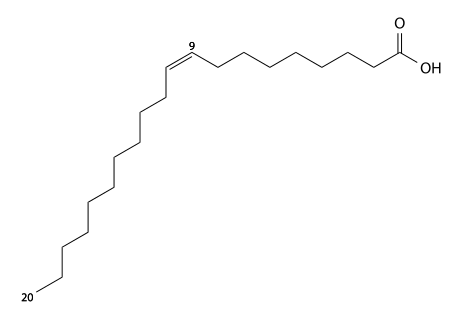
| ω−7 | Paullinic acid | C20:1 | Δ13 | CH3(CH2)5CH=CH(CH2)11COOH | cis | guarana[13] |
| ω−9 | Oleic acid | C18:1 | Δ9 | CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)7COOH | cis | olive oil, pecan oil,[14] canola oil[15] |
| ω−9 | Elaidic acid | C18:1 | Δ9 | CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)7COOH | trans | hydrogenated vegetable oil[16] |
| ω−9 | Gondoic acid | C20:1 | Δ11 | CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)9COOH | cis | jojoba oil[17] (edible but non-caloric and non-digestible) |
| ω−9 | Erucic acid | C22:1 | Δ13 | CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)11COOH | cis | wallflower seed, mustard oil |
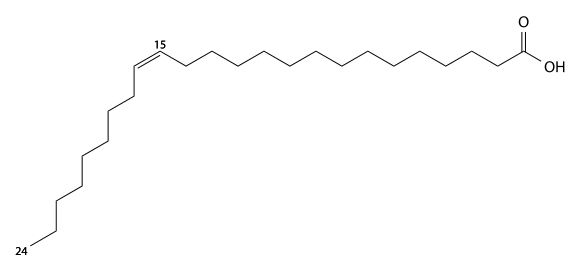
| ω−9 | Nervonic acid | C24:1 | Δ15 | CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)13COOH | cis | King salmon, flaxseed, sockeye salmon, sesame seed, macadamia nuts[18] |
| ω−9 | Mead acid | C20:3 | Δ5,8,11 | CH3(CH2)7CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CH(CH2)3COOH | cis | cartilage |
Fatty acid molecular species[edit]
Mono-unsaturated fatty acid[edit]
The following fatty acids have one unsaturated bond.
Crotonic acid[edit]
Crotonic acid has 4 carbons, is included in croton oil, and is a trans-2-mono-unsaturated fatty acid. C3H5 CO2H, IUPAC organization name (E)-but-2-enoic acid, trans-but-2-enoic acid, numerical representation 4:1, n-1, molecular weight 86.09, melting point 72–74 °C, boiling point 180–181 °C, specific gravity 1.027. CAS registry number 107-93-7.
Myristoleic[edit]
Myristoleic acid has 14 carbons, is found in whale blubber, and is a cis-9-monounsaturated fatty acid. C13H25CO2H, IUPAC organization name (Z)-tetradec-9-enoic acid, numerical representation 14:1, n-5, molecular weight 226.36, melting point of −4.5 – −4 °C. CAS Registry Number 544-64-9.
Palmitoleic acid[edit]
Palmitoleic acid has 16 carbons, is found in cod liver oil, sardine oil, and herring oil, and is a cis-9-monounsaturated fatty acid. C15H29CO2H, IUPAC organization name (Z)-hexadec-9-enoic acid, n-7, numerical representation of 16:1, molecular weight 254.41, melting point 5 °C, specific gravity 0.894. CAS Registry Number 373-49-9.
Sapienic acid[edit]
Sapienic acid has 16 carbons, is found in the skin, and is a cis-6-mono-unsaturated fatty acid. C15H29CO2H, IUPAC organization name (Z)-6-Hexadecenoic acid, n-10, numerical expression 16:1, molecular weight 254.41. CAS Registry Number 17004-51-2.
Oleic acid[edit]
Oleic acid has 18 carbons, is found in most animal fats and olive oil, and is a cis-9-monounsaturated fatty acid. C17H33CO2H, IUPAC organization name (Z)-octadec-9-enoic acid, numerical representation 18:1 (9), n-9, molecular weight 282.46, melting point 13.4 °C, specific gravity 0.891. CAS Registry Number 112-80-1.
Elaidic acid[edit]
Elaidic acid has 18 carbons and is a trans-9-mono-unsaturated fatty acid. It is also a trans isomer of oleic acid. C17H33CO2H, IUPAC organization name (E)-octadec-9-enoic acid, numerical representation 18:1 (9), n-9, molecular weight 282.46, melting point 43–45 °C. CAS Registry Number 112-79-8.
Vaccenic acid[edit]
Vaccenic acid has 18 carbons, is found in beef tallow, mutton, and butter, and is a trans-11-mono-unsaturated fatty acid. C17H33CO2H, IUPAC organization name (E)-octadec-11-enoic acid, numerical representation 18:1 (11) n-7, molecular weight 282.46. CAS Registry Number 506-17-2.
Gadoleic acid[edit]
Gadoleic acid has 20 carbons, is found in cod liver oil and other marine animal oils, and is a cis-9-mono-unsaturated fatty acid. C19H37CO2H, IUPAC organization name (Z)-icos-9-enoic acid, numerical representation 20:1 (9), n-11, molecular weight 310.51. CAS Registry Number 29204-02-2.
Eicosenoic acid[edit]
Eicosenoic acid has 20 carbons, is found in a wide variety of plant oils, and is a cis-11-mono-unsaturated fatty acid. C19H37CO2H, IUPAC organization name (Z)-icos-11-enoic acid, numerical representation 20:1 (11), n-9, molecular weight 310.51. CAS Registry Number 5561-99-9.
Erucic acid[edit]
Erucic acid has 22 carbons, is found in rapeseed oil and mustard oil, and is a cis-13-monounsaturated is a fatty acid. C21H41CO2H, IUPAC organization name (Z)-docos-13-enoic acid, numerical representation 22:1, n-9, molecular weight 338.57, melting point 33–35 °C. CAS Registry Number 112-86-7.
Nervonic acid[edit]
Nervonic acid has 24 carbons, is found in brain glycolipids (Nervon) and sphingomyelin, and is a cis-15-mono-unsaturated fatty acid. C23H45CO2H, IUPAC organization name (Z)-tetracos-15-enoic acid, numerical representation 24:1, n-9, molecular weight 366.62, melting point 42–43 °C. CAS Registry Number 506-37-6.
Di-unsaturated fatty acid[edit]
The following fatty acids have two unsaturated bonds.
Linoleic acid[edit]
Linoleic acid has 18 carbons, is contained in many vegetable oils, particularly semi-drying oils, and is a cis-9-cis-12-di-unsaturated fatty acid. C17H31CO2H, IUPAC organization name (9Z, 12Z)-octadeca-9,12-dienoic acid, numerical representation 18:2 (9,12), n-6, molecular weight 280.45, melting point −5 °C, specific gravity 0.902. CAS Registry Number 60-33-3. There are isomers of linoleic acid with double bonds separated by one single bond. They are named conjugated linoleic acids.
Eicosadienoic acid[edit]
Eicosadienoic acid (eicosadienoic's) has 20 carbons and is a cis-11-cis-14-di-unsaturated fatty acid. C19H35CO2H, IUPAC organization name (11Z, 14Z)-icosa-11,14-dienoic acid, numerical representation 20:2 (11,14), n-6, molecular weight 308.50.
Docosadienoic acid[edit]
Docosadienoic acid (docosadienoic's) has 22 carbons and is a cis-13-cis-16-di-unsaturated fatty acid. C21H39CO2H, IUPAC organization name (13Z, 16Z)-docosa-13,16-dienoic acid, numerical representation 22:2 (13,16), n-6, molecular weight 336.55. CAS Registry Number 7370-49-2.
Tri-unsaturated fatty acids[edit]
The following fatty acids have three unsaturated bonds.
Linolenic acid[edit]
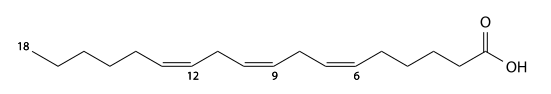
α-Linolenic acid (alpha-linolenic's) has 18 carbons, is found in linseed oil and drying oil, and is a 9,12,15-tri-unsaturated fatty acid. C17H29CO2H, IUPAC organization name (9Z, 12Z, 15Z)-octadeca-9,12,15-trienoic acid, numerical representation 18:3 (9,12,15), n-3, molecular weight 278.43, melting point −11 °C, specific gravity 0.914. CAS Registry Number 463-40-1.
γ-Linolenic acid (gamma-linolenic's) has 18 carbons, is the structural isomer of α-linolenic acid. IUPAC organization name (6Z, 9Z, 12Z)-octadeca-6,9,12-trienoic acid, numerical representation 18:3 (6,9,12), n-6. CAS Registry Number 506-26-3.
Pinolenic acid[edit]
Pinolenic acid (pinolenic's) has 18 carbons, is found in pine nuts, and is a 5,9,12-triunsaturated fatty acid. C17H29CO2H, IUPAC organization name (5Z, 9Z, 12Z)-octadeca-5,9,12-trienoic acid, numerical representation 18:3 (5,9,12), n-6, molecular weight 278.43. CAS Registry Number 16833-54-8.
Eleostearic acid[edit]
α-Eleostearic acid (alpha-eleostearic's) has 18 carbons, is found in Kiri drying oil, and is a 9,11,13-triunsaturated fatty acid. C17H29CO2H, IUPAC organization name (9Z, 11E, 13E)-octadeca-9,11,13-trienoic acid, numerical representation 18:3 (9,11,13), n-5, molecular weight 278.43.
β-Eleostearic acid (beta-eleostearic's, beta-eleostearic acid) is a geometric isomer of α-eleostearic acid. IUPAC organization name (9E, 11E, 13E)-octadeca-9,11,13-trienoic acid, numerical representation 18:3 (9,11,13), n-5.

α- and β-Eleostearic acids are cis–trans isomers. Other cis–trans isomers of eleostearic acid are:
Catalpic acid (9E, 11E, 13Z)
Punicic acid (9Z, 11E, 13Z).
Mead acid[edit]
Mead acid (Mead's) has 20 carbons, is a 5,8,11-tri-unsaturated fatty acid. C19H33CO2H, IUPAC organization name (5Z, 8Z, 11Z)-icosa-5,8,11-trienoic acid, numerical representation 20:3 (5,8,11), n-9, molecular weight 306.48. CAS Registry Number 20590-32-3.
Dihomo-γ-linolenic acid[edit]
Dihomo-γ-linolenic acid (dihomo-gamma-linolenic's, dihomo-gamma-linolenic acid, DGLA) has 20 carbons, and is an 8,11,14-tri-unsaturated fatty acid. C19H33CO2H, IUPAC organization name (8Z, 11Z, 14Z)-icosa-8,11,14-trienoic acid, numerical representation 20:3 (8,11,14), n-6, molecular weight 306.48. CAS Registry Number 1783-84-2.
Eicosatrienoic acid[edit]
Eicosatrienoic acid (eicosatrienoic's, eicosatrienoic acid) has 20 carbons and is an 11,14,17- tri unsaturated fatty acid. C19H33CO2H, IUPAC organization name (11Z, 14Z, 17Z)-icosa-11,14,17-trienoic acid, numerical representation 20:3 (11,14,17), n-3, molecular weight 306.48.
Tetra-unsaturated fatty acids[edit]
The following fatty acids have four unsaturated bonds.
Stearidonic acid[edit]
Stearidonic acid (stearidonic's) has 18 carbons, is found in sardine oil and herring oil, and is a 6,9,12,15-tetraunsaturated fatty acid. C17H27CO2H, IUPAC organization name (6Z, 9Z, 12Z, 15Z)-octadeca-6,9,12,15-tetraenoic acid, numerical representation 18:4 (6,9,12,15), n-3, molecular weight 276.41. CAS Registry Number 20290-75-9.
Arachidonic acid[edit]
Arachidonic acid (arachidonic's) has 20 carbons, is present in animal visceral fat (brain, liver, kidney, lung, spleen), and is a 5,8,11,14-tetra-unsaturated fatty acid. C19H31CO2H, IUPAC organization name (5Z, 8Z, 11Z, 14Z)-icosa-5,8,11,14-tetraenoic acid, numerical representation 20:4 (5,8,11,14), n-6, molecular weight 304.47, boiling point 169–171 °C. CAS Registry Number 506-32-1.
In signal transduction, arachidonic acid is produced through decomposition of the phospholipid cell membrane. This gives rise to the arachidonic acid cascade, a metabolic pathway that yields lipid mediator compounds[19] such as prostaglandins, thromboxanes and leukotrienes. This pathway has attracted study for its key role in inflammatory diseases such as asthma.[20]
Eicosatetraenoic acid[edit]
Eicosatetraenoic acid (eicosatetraenoic's) has 20 carbons and is an 8,11,14,17-tetraunsaturated fatty acid. C19H31CO2H, IUPAC organization name (8Z, 11Z, 14Z, 17Z)-icosa-8,11,14,17-tetraenoic acid, numerical representation 20:4 (8,11,14,17), n-3, molecular weight 304.47.
Adrenic acid[edit]
Adrenic acid (adrenic'sd) has 22 carbons and is a 7,10,13,16-tetra-unsaturated fatty acid. C21H35CO2H, IUPAC organization name (7Z, 10Z, 13Z, 16Z)-docosa-7,10,13,16-tetraenoic acid, numerical representation 22:4 (7,10,13,16), n-6, molecular weight 332.52. CAS Registry Number 28874-58-0.
Penta-unsaturated fatty acids[edit]
The following fatty acids have five unsaturated bonds.
Bosseopentaenoic acid[edit]
Bosseopentaenoic acid (Boseopentaen's), has 20 carbons and is a 5,8,10,12,14-pentaunsaturated fatty acid. C17H25CO2H, IUPAC organization name (5Z, 8Z, 10E, 12E, 14Z)-eicosa-5,8,10,12,14-pentaenoic acid, numerical representation 20:5 (5,8,10,12,14), n-6, molecular weight 302.46 g·mol−1.[21]
Eicosapentaenoic acid[edit]
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) has 20 carbons, is found in fish oil, is a pentaunsaturated fatty acid. It is one of the essential fatty acids. The recommendation of ingesting fish oil supplements during pregnancy is said to help increase the cognitive ability at 6 months, but mercury concentration in fish products offsets the effect. In patients with hyperlipidemia and obstructive artery disease it can help lower triglycerides and also has an anti-platelet effect similar to other anti-platelet agents. It has also been shown to help in secondary prevention of ischemic heart disease as shown with the JELIS test.
C19H29CO2H, IUPAC organization name (5Z, 8Z, 11Z, 14Z, 17Z)-icosa-5,8,11,14,17-pentaenoic acid, numerical representation of 20:5 (5,8,11,14,17), n-3, molecular weight 302.45, melting point −54 – −53 °C, specific gravity 0.943. CAS Registry Number 10417-94-4.
Ozubondo acid[edit]
Ozubondo acid (Ozubondo's, Osbond acid), has 22 carbons, is a 4,7,10,13,16- pentaunsaturated fatty acid. C21H33CO2H, IUPAC organization name (4Z, 7Z, 10Z, 13Z, 16Z)-docosa-4,7,10,13,16-pentaenoic acid, numerical representation 22:5 (4,7,10,13,16), n-6, molecular weight 330.50. CAS Registry Number 25182-74-5
Sardine acid[edit]
Sardine acid (clupanodonic acid) has 22 carbons, is found in sardine oil and herring oil, is a 7,10,13,16,19- pentaunsaturated fatty acid. C21H33CO2H, IUPAC organization name (7Z, 10Z, 13Z, 16Z, 19Z)-docosa-7,10,13,16,19-pentaenoic acid, numerical representation 22:5 (7,10,13,16,19), n-3, molecular weight 330.50.
Tetracosapentaenoic acid[edit]
Tetracosapentaenoic acid has 24 carbons, is a 9,12,15,18,21-penta unsaturated fatty acid. C23H37CO2H, IUPAC organization name (9Z, 12Z, 15Z, 18Z, 21Z)-tetracosa-9,12,15,18,21-pentaenoic acid, numerical representation 24:5 (9,12,15,18,21), n-3, molecular weight 358.56.
Hexa-unsaturated fatty acids[edit]
The following fatty acids have six unsaturated bonds.
Cervonic acid[edit]
Cervonic acid (or docosahexaenoic acid) has 22 carbons, is found in fish oil, is a 4,7,10,13,16,19-hexa unsaturated fatty acid. In the human body its generation depends on consumption of omega 3 essential fatty acids (e.g., ALA or EPA), but the conversion process is inefficient.[22] C21H31CO2H, IUPAC organization name (4Z, 7Z, 10Z, 13Z, 16Z, 19Z)-docosa-4,7,10,13,16,19-hexaenoic acid, numerical representation 22:6 (4,7,10,13,16,19), n-3, molecular weight 328.49, melting point −44 °C, specific gravity 0.950. CAS Registry Number 6217-54-5.
Herring acid[edit]
Herring acid (Herring's, Nisinic acid) is a 6,9,12,15,18,21-hexa unsaturated fatty acid with 24 carbon atoms. C23H35CO2H, IUPAC organization name (6Z, 9Z, 12Z, 15Z, 18Z, 21Z)-tetracosa-6,9,12,15,18,21-hexaenoic acid, numerical representation 24:6 (6,9,12,15,18,21), n-3, molecular weight 356.54.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ Simopoulos, Artemis P. (2002). "Omega‐3 fatty acids in wild plants, nuts and seeds". Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 11 (s6): S163–S173. doi:10.1046/j.1440-6047.11.s.6.5.x.
- ^ Guesnet P, Alessandri JM (2011). "Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and the developing central nervous system (CNS) - Implications for dietary recommendations". Biochimie. 93 (1): 7–12. doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2010.05.005. PMID 20478353.
- ^ Oil, peanut, salad or cooking: search for peanut oil on "USDA Food Composition Databases". Archived from the original on 2015-03-03. Retrieved 2011-11-14.
- ^ M. K. Nutter, E. E. Lockhart and R. S. Harris (1943). "The chemical composition of depot fats in chickens and turkeys". Journal of the American Oil Chemists' Society. 20 (11): 231–234. doi:10.1007/BF02630880. S2CID 84893770.
- ^ "Olive Oil : Chemical Characteristics".
- ^ Beltran; Del Rio, C; Sánchez, S; Martínez, L; et al. (2004). "Influence of Harvest Date and Crop Yield on the Fatty Acid Composition of Virgin Olive Oils from Cv. Picual" (PDF). J. Agric. Food Chem. 52 (11): 3434–3440. doi:10.1021/jf049894n. PMID 15161211.
- ^ "Conditions We Treat".
- ^ Flider, Frank J. (2013). "Development and commercialization of GLA safflower oil". Lipid Technology. 25 (10): 227–229. doi:10.1002/lite.201300302.
- ^ Horrobin, D. F., 1990a. Gamma linolenic acid. Rev. Contemp. Pharmacother. 1, 1-45
- ^ Huang, Y.-S. and Mills, D. E. (Eds.), 1996. Gamma-linolenic acid metabolism and its roles in nutrition and medicine. AOCS Press, Champaign, Illinois, 319 pp.
- ^ "Nuts, macadamia nuts, raw". NutritionData.com.
- ^ Natural trans fats may be good for you. May 19, 2008
- ^ Avato, P; Pesante, MA; Fanizzi, FP; Santos, CA (2003). "Seed oil composition of Paullinia cupana var. Sorbilis (Mart.) Ducke". Lipids. 38 (7): 773–80. doi:10.1007/s11745-003-1126-5. PMID 14506841. S2CID 4026737.
- ^ Villarreal-Lozoya, Jose E.; Lombardini, Leonardo; Cisneros-Zevallos, Luis (2007). "Phytochemical constituents and antioxidant capacity of different pecan Carya illinoinensis (Wangenh.) K. Koch] cultivars". Food Chemistry. 102 (4): 1241. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.07.024.
- ^ "Comparison of Dietary Fats Chart". Canola Council of Canada. Archived from the original on 2008-06-06. Retrieved 2008-09-03.
- ^ Abbey M, Nestel PJ (1994). "Plasma cholesteryl ester transfer protein activity is increased when trans-elaidic acid is substituted for cis-oleic acid in the diet". Atherosclerosis. 106 (1): 99–107. doi:10.1016/0021-9150(94)90086-8. PMID 8018112.
- ^ Miwa, Thomas (1971). "Jojoba Oil Wax Esters and Derived Fatty Acids and Alcohols: Gas Chromatographic Analyses". Journal of the American Oil Chemists' Society. 48 (6): 259–264. doi:10.1007/bf02638458. S2CID 1466516. Retrieved May 6, 2013.
- ^ "Foods highest in 24:1 C".
- ^ Edwards; McCarthy; Wenceslau (2020). "ch. 3.1: Arachidonic Acid-Derived Bioactive Lipids". Current Pharmaceutical Design. 26 (30): 3723–3732. doi:10.2174/1381612826666200417150121. PMC 7542659.
- ^ Wang, B.; Wu, L.; Chen, J; et al. (2021). "Metabolism pathways of arachidonic acids". Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy. 6 (64). doi:10.1038/s41392-020-00443-w. PMC 7910446.
- ^ Burgess, J.R.; De la Rosa, R.I.; Jacobs, R.S.; Butler, A (1991). "A new eicosapentaenoic acid formed from arachidonic acid in the coralline red algae Bossiella orbigniana". Lipids. 26 (2): 1057–1059. doi:10.1007/BF02544012
- ^ Gropper, Sareen Annora Stepnick; Smith, Jack L.; Carr, Timothy P. Advanced nutrition and human metabolism (7 ed.). Australia. ISBN 9781305627857. OCLC 988914315.